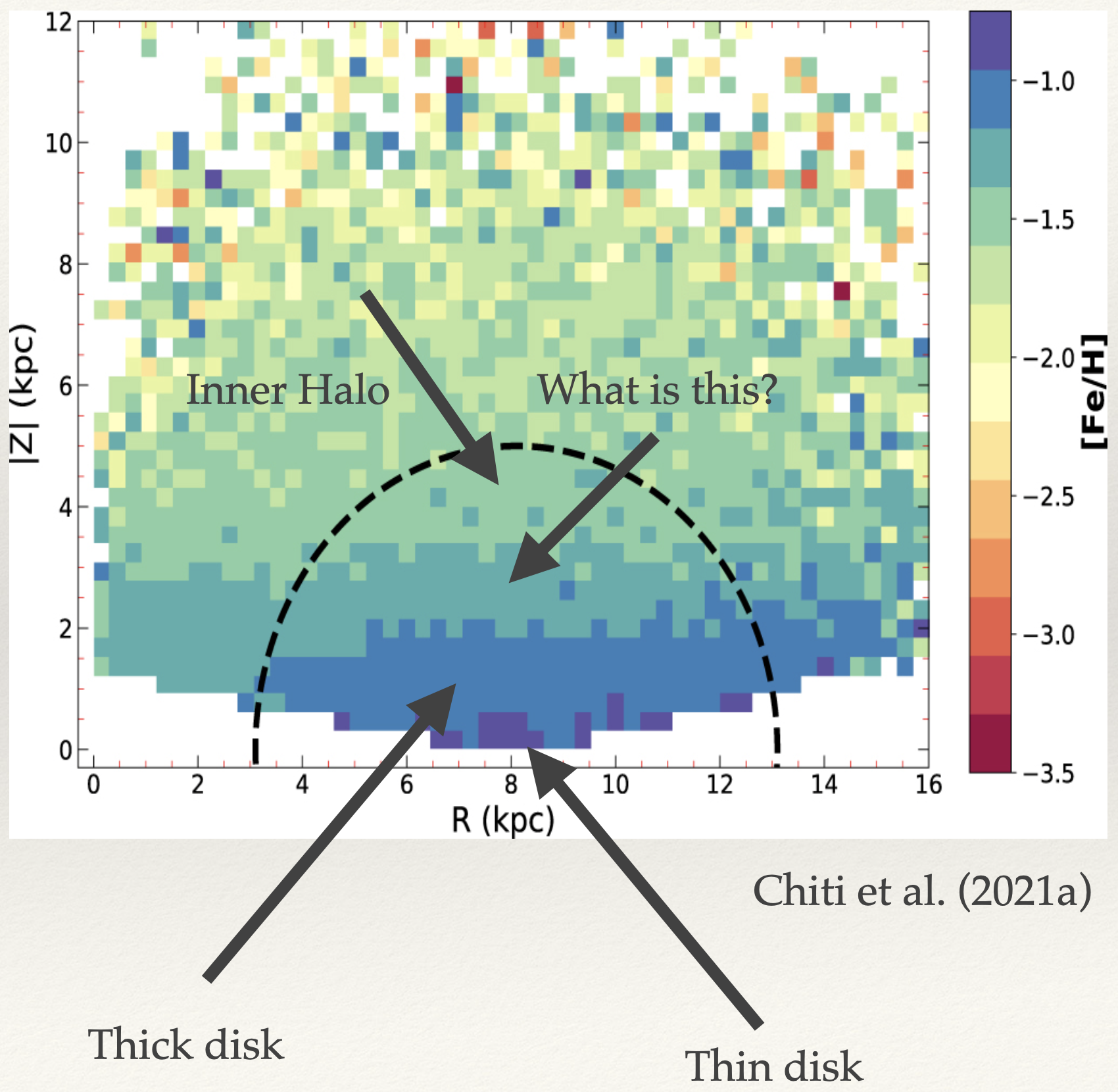
Atari disk
Atari 辺り in Japanese means “nearby” or “neighborhood” in reference to it sharing close space with the Galactic thin and thick disks. It was found by searching through the kinematics of metal-poor stars currently located in the Galactic disk. The properties of the Atari disk indicate spatial co-existence in the same vicinity as the other disk components, but it was the remnant of a radial merger with our Galaxy a long time ago.
Summary of the findings:
-
Discovery of 41 stars with [Fe/H] <-3.0; including five with [Fe/H] <-4.0
-
An independent component of the Galactic disk
-
Remnant of a completely disrupted satellite that radially plunged into the early Milky Way Progenitor mass is only < 109 M⊙
Summary of the properties:
-
Atari disk has rotational velocity ≈154 km/s
-
[Fe/H] depends on the vertical and radial distances.
-
Intermediate orbital eccentricities values sets between thick disk and halo values.
-
Less extended but more puffed up than the other disk components: hR = 2.48 kpc, hZ = 1.67 kpc